# 4. CSS选择器
CSS选择器的作用是找出某类元素,以便设置对应的样式。


# * 选择所有元素(0000)
选择器 * 可以匹配所有元素,CSS2。相关css hack: My favorite CSS hack (opens new window)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 4px;
}
/* css hack: 根据背景显示页面的层级关系 */
* { background-color: rgba(255,0,0,.2); }
* * { background-color: rgba(0,255,0,.2); }
* * * { background-color: rgba(0,0,255,.2); }
* * * * { background-color: rgba(255,0,255,.2); }
* * * * * { background-color: rgba(0,255,255,.2); }
* * * * * * { background-color: rgba(255,255,0,.2); }
* * * * * * * { background-color: rgba(255,0,0,.2); }
* * * * * * * * { background-color: rgba(0,255,0,.2); }
* * * * * * * * * { background-color: rgba(0,0,255,.2); }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
</html>

# id选择器(0100)
<!-- #<id值>,<元素名>.#<id值> -->
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
#myanchor {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 4px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a id="myanchor" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
# 类、属性、伪类选择器(0010)
# 类(class)选择器
选择器 .<类名> 或 *.<类名>, <元素名>.<类名>,css1。
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
.class1 {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 4px;
}
span.class2 { /* 选择span元素且类为class2的元素*/
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>

# 属性选择器
[属性名或属性条件] 或 <元素名>[属性名或属性条件],匹配有该属性 或者 属性满足指定条件的元素。

<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
[href] { /* 匹配有href属性的元素 */
border: thin black solid;
padding: 4px;
}
[href="http://baidu.com"] { /* 匹配href属性值为http://baidu.com的元素 */
color: red;
}
[id^="p"] { /* 匹配id属性值以p开头的元素 */
color: #ff00ff;
}
[id$="2"] { /* 匹配id属性值以2结尾的元素 */
border:1px solid #000;
}
[class~="class3"] { /* 如果class属性的值其中一个值等于class3的元素 */
color: blue;
}
[lang|="en"] { /* 匹配lang="en-us",lang="en-gb" 的元素 */
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2 class3">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<p class="class3">I like apples and oranges 2.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
<p>Today is monday 1.</p>
<p id="p1">Today is monday 2.</p>
<p id="p2">Today is monday 3.</p>
<p id="p3">Today is monday 4.</p>
</body>

# 伪类选择器
伪类选择器和伪元素一样,并不是直接针对文本元素的,而是方便处理某些共同特征的元素。
# 结构性伪类选择器
# :root 文档根元素
:root选择器匹配文档中的根元素,总是返回html元素,CSS3。
# :first-child等子元素
- :first-child 选择元素的第一个子元素,CSS2
- :last-child 选择元素的最后一个子元素,CSS3
- :only-child 选择元素的唯一子元素,CSS3
- :only-of-type 选择元素指定类型的唯一子元素,CSS3
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* :root {} 等价于 html {} */
:root {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 4px;
}
/*
* 注意,这里不是p元素的第一个子元素
* 而是 匹配某个元素的第一个子元素,且为p,一般用来缩小范围。
*/
p:first-child {
color: red;
}
/* p元素的最后一个子元素, 且为span。*/
p > span:last-child {
color: blue;
}
p:only-child { /* p元素,且该父元素只有该元素一个子元素 */
border: 1px dashed #000;
}
/* 某个父元素只有一个子元素section,本例子中匹配不到,除非删除一个section */
section:only-of-type {
border:1px solid red;
padding:10px;
}
/* 某个父元素只有一个子元素div */
div:only-of-type {
color:purple;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and <span>oranges</span>.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
<section>
<p>section的第一个子元素,且为p, p:first-child</p>
</section>
<section>
第二个section
</section>
<div>
div:only-of-type,该div的父元素的子元素,只有一个div,就是当前div
</div>
</body>

# :nth-child 等指定索引子元素
- :nth-child(n) 选择父元素的第n个子元素
- :nth-last-child(n) 选择父元素的倒数第n个子元素
- :nth-of-type(n) 选择父元素定义类型的第n个子元素
- :nth-last-of-type(n) 选择父元素定义类型的倒数第n个子元素
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 某个父元素的第一个子元素,且为p */
p:nth-child(1) {
color: red;
}
/* 某个父元素的第二个子元素,且为span*/
span:nth-child(2) {
color: blue;
}
/* 某个元素的倒数第二个子元素,且为span */
span:nth-last-child(2) {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
/* 父元素的第2个该类型(section)的子元素 */
section:nth-of-type(2) {
border: thin dashed #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and <span>oranges</span>.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
<section>
<p>section的第一个子元素,且为p, p:first-child</p>
</section>
<section>
第二个section
</section>
<div>
div:only-of-type,该div的父元素的子元素,只有一个div,就是当前div
</div>
</body>

# UI伪类选择器

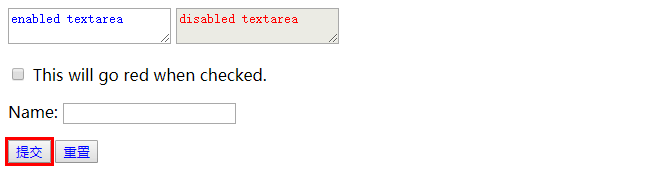
# :enabled或:disabled选择器
选择启用或禁用的元素。这些元素一般是用来收集用户输入的。
# :checked, :default
- :checked已勾选的元素
- :default默认元素
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 包括未disabled的input、button */
:enabled {
color: blue;
}
:disabled {
color: red;
}
/* 元素选中后,该元素之后相邻的元素设置为红色 */
:checked + span {
color: red;
}
/* 从一组类似的元素中选择默认元素,提交按钮,总是表单的默认按钮*/
:default {
outline: medium solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<textarea>enabled textarea</textarea>
<textarea disabled>disabled textarea</textarea>
<p>
<input type="checkbox" name="apples"> <span>This will go red when checked.</span>
</p>
<form>
<p>Name: <input name="name" ></p>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
<button type="reset">重置</button>
</form>
</body>
# :valid和:invalid
:valid和:invalid选择器分别匹配符和和不符和他们的输入验证要求的input元素。
# :in-range或:out-of-range
:in-range 匹配在正常范围内的选择器。:out-of-range匹配超出范围的元素
# :required或:optional
:required 匹配具有required属性的input元素。:optional 匹配可填可不填的表单元素
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 如果前面不加form,form这个元素也会被加上样式 */
form :valid {
outline: medium solid green;
}
form :invalid {
outline: medium solid red;
}
:in-range {
color: blue;
}
:out-of-range {
color:red;
}
:required {
width: 300px;
}
:optional {
width:100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="http://zuo11.com">
<p>Name: <input name="name" required></p>
<p>age: <input name="age"></p>
<p>
已婚 <input type="checkbox" name="married" required>
</p>
<p>在正常范围内:<input type="number" name="n1" min="10" value="20"></p>
<p>非正常范围内:<input type="number" name="n2" min="10" value="5"></p>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
<button type="reset">重置</button>
</form>
</body>

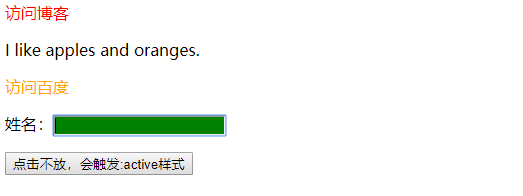
# 动态伪类选择器
# :link和:visited选择a标签
:link默认a标签的样式,:visited已访问过的a元素
/* 浏览器默认的a样式*/
a:link {
color: blue;
text-decoration: underline;
}
# :hover, :active和:focus选择器
- :hover 鼠标悬停到对应的元素后的样式
- :active 当前被用户激活的元素,点击a、button标签不放,或点击p标签都会触发:active的样式
- :focus 匹配当前获得焦点的元素
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
a:link { /* a标签的默认样式*/
color: red;
text-decoration: none; /*去掉下划线 */
}
a:visited { /* 访问过的a标签 */
color: orange;
}
span:hover { /* 鼠标悬停在p标签上,p的样式如下 */
border: thin black solid;
}
button:active {
outline: thin dashed red;
}
:focus {
background: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
<p>
<p>姓名:<input name="name" autocomplete="off"> </p>
<button>点击不放,会触发:active样式</button>
</p>
</body>
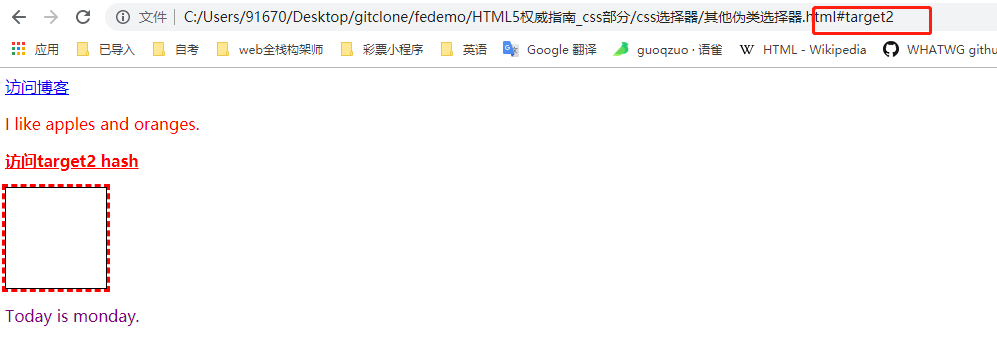
# 其他伪类选择器
# :not(选择器)
否定选择器, CSS3。
# :empty, :lang, :target
- :empty 选择内容为空的元素(匹配没有任何内容的元素)
- :lang(目标语言) 根据语言选择元素({lang|=目标语言])
- :target 选择URL片段(hash #target2)指向的元素,通过#hash跳转到该id的位置,该id的元素就是:target匹配的元素
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
:not([class*="class2"]) { /* class不包含class2的元素 */
color: red;
}
:empty { /* 匹配没有任何内容的元素 */
margin-top: 1em;
outline: medium dashed red;
}
:lang(en) {
color: purple;
}
:target {
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a id="target1" class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a id="target2" href="#target2">访问target2 hash</a>
<div style="width:100px;height:100px;border:1px solid #000;"></div>
<p lang="en-uk">Today is monday. </p>
</body>
# 元素、伪元素选择器(0001)
# 元素名选择器
指定元素名(元素类型)为选择器可以选取文档中该元素的所有实例,css1。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
a {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 4px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
</html>
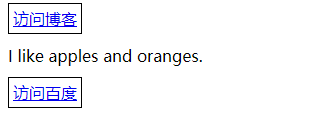
# 伪元素选择器
伪选择器(peseudo-selector)提供了更复杂的功能,伪选择器分两种:伪元素和伪类。伪元素实际不存在,他们是css提供的额外"福利",方便选中文档内容。
# ::first-line,::first-letter
- ::first-line选择器, 本内容的首行,css1。
- ::first-letter选择器,文本块的首字母,css1。
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
::first-line {
color: blue;
}
p::first-line {
color: red;
}
::first-letter {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
(1)Fourscore and seven years ago our fathers brought forth
on this continent a new nation. conceived in liberty, and
dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.
</p>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<section>
(2)Fourscore and seven years ago our fathers brought forth
on this continent a new nation. conceived in liberty, and
dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.
</section>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>

# :before和:after选择器
:before 在选中元素的内容之前插入内容, :after 在选中元素的内容之后插入内容, css2。
# css计数器counter
counter-reset: paracount。初始化名为paracount的计数器,默认值为0, counter-reset: paracount 10, 初始值为10。p355
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 为a标签前后加入内容 */
a:before {
content: "点击 ";
color: #000;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
a:after {
content: " !";
color:red;
}
/* 为p增加前置的计数 */
body {
counter-reset: paracount;
}
p:before {
content: counter(paracount) ". ";
counter-increment: paracount;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<p>Today is monday.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
# 复合选择器
# 并集(组合)选择器
<选择器>,<选择器>,<选择器>,创建由逗号分隔的多个选择器可以将同样的样式应用到多个选择器。
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
a,[class*="ss2"] {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 4px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span class="class2">apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
# 后代选择器
// <第一个选择器> <第二个选择器> 第一个选择器 后代元素中满足第二个选择器的元素。
# 选择子元素
// <第一个选择器> > <第二个选择器>
# 选择兄弟元素
// <第一个选择器> + <第二个选择器> 需要是第一个选择器的兄弟元素,且在该元素之后紧跟。
// <第一个选择器> ~ <第二个选择器> 需要是第一个选择器的兄弟元素,且在该元素之后,不用紧跟。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>css选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
p span {
color: red;
}
table td { /* 后代元素 */
color: blue;
}
table > th { /* table没有th子元素,只有th的后代元素,样式不生效*/
color: red;
}
table + a { /* table后面没有紧跟的a元素,所以样式无效*/
border: 1px solid #000;
}
table + p { /* 匹配table元素后面紧跟的兄弟元素p */
border: 1px solid #000;
}
table ~ a { /* table后面兄弟元素a,不用紧跟,但需要在table之后 */
border: 1px dashed #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="class1 class2" href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span>apples</span> and <span>oranges.</span></p>
<p><a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a></p>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>张三</td>
<td>23</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>李四</td>
<td>56</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>table后面的一个兄弟元素p</p>
<a>table后面的一个兄弟元素a</a>
</body>
</html>
