# 2. 初探CSS
CSS(层叠样式表)用来规定HTML文档的呈现形式(外观和格式编排)

# 定义和应用样式
# css样式
css样式由一条或多条以分号隔开的样式声明组成。
/* 每条声明都包含属性和值。 */
background: grey;
color: white;
# 使用元素内嵌样式(Inline)
使用元素的全局属性style, 将样式直接应用到元素
<a href="http://zuo11.com" style="background:grey;color:white;">访问博客</a>
# 使用文档内嵌样式(Internal)
直接对元素应用简单方便,但对于可能大量需要各种样式的复杂文档来说缺乏效率。需要一个元素一个元素加,且耦合性高,不利于维护。可以使用style元素定义文档内嵌样式,通过css选择器指示浏览器应用样式。
<head>
<title>文档内嵌样式</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 这里的a css为选择器, 为每一个a元素应用样式 */
a {
background: grey;
color: white;
}
span {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
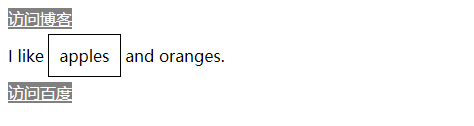
# 使用外部样式表(External)
如果有一套样式要用于多个文档,那么逾期在每一个文档中重复定义相同的样式,不如另外创建一个独立的样式表文件。这种文件按惯例已.css为文件扩展名。
/* 文件style.css内容 */
a {
background: grey;
color: white;
}
span {
border: thin black solid;
padding: 10px;
}
导入外部样式表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>文档内嵌样式</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css"></link>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://zuo11.com">访问博客</a>
<p>I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.</p>
<a href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
</html>
# @import 从样式表中导入样式
下面的例子中从style.css中导入样式到common.css
/* 注意句子结束一定要加分号;*/
@import "style.css";
span {
border: medium black dashed;
color: red;
}
示例
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="common.css"></link>
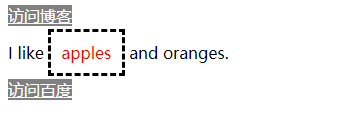
# 指定样式表字符编码
如果样式表中未声明字符编码,默认为编码为"utf-8",如果有指定,就会用指定的编码。
@charset "UTF-8";
@import "style.css";
span {
border: medium black dashed;
}
# 样式的层叠和继承
前面讲过了三种定义样式的方式(元素内嵌,文档内嵌,外部样式),还有两种是浏览器样式和用户样式。如果用各种方式声明了同样的样式属性,但值不同,浏览器怎么确定具体以哪个样式值来渲染元素呢?这就需要弄清楚样式层叠、继承的规则。
# 浏览器样式
- 浏览器样式(用户代理样式)是元素尚未设置样式时浏览器默认的样式。不同的浏览器可能会有差异,以button为例,Firefox和Chrome默认的button样式就不一样。一般a的浏览器的默认样式为:
a {
color: blue;
text-decoration: underline;
}
- 用户样式(书中记载的自定义样式文件没找到,暂时忽略)
# 样式如何层叠
浏览器显示元素时,获取CSS样式属性值的次序如下:
- 元素内嵌样式(用元素的全局属性style定义的样式)
- 文档内嵌样式(定义在style元素中的样式)
- 外部样式(用link导入的样式)
- 浏览器样式(浏览器默认样式)
英文参考:https://www.w3schools.com/html/html_css.asp
- Inline - by using the style attribute in HTML elements
- Internal - by using a <style> element in the <head> section
- External - by using an external CSS file
会根据顺序一层一层找,如果在1找到了对应的属性值,那么2,3,4设置的相同的属性值会失效。
# !important调整层叠次序
如果把样式属性标记为重要(!important),可以改变正常的层叠次序
<style>
a { color: red !important; } /* 最终会以该样式为准 */
</style>
<a href="http://zuo11.com" style="color: blue;">访问链接</a>
# 根据特殊性和定义次序解决同级样式冲突
如果两条定义于同一层次的样式都能应用于同一个元素。且都包含同样的属性值,就需要根据来决特殊性定到底使用哪种。
- a. 样式的选择器中id值的数目(#)
- b. 选择器中其他属性和伪类的数目(.class等属性)
- c. 选择器中元素名和伪元素数目(元素名等)
a的特殊性最高,b其次,c最低。按a-b-c来表示。比如如果a值相等,才会去比较b。1-0-0的特殊性比0-5-5高。在 <<CSS权特威指南>> 中,有4位,最高位为内嵌(Inline)样式设置的样式。关于特殊性,建议看CSS权威指南,个人认为比这里要好理解一点。如果层级一样,谁后定义的,优先级就越高。
<body>
<style>
a { color: red; } /* 0-0-1*/
a.myclass { /* 0-1-0 */
color: blue ;
}
</style>
<a href="http://zuo11.com">访问链接</a>
<a class="myclass" href="http://baidu.com">访问百度</a>
</body>
# 继承(inherit)
如果浏览器在直接相关的样式中找不到某个属性的值,就会求助于继承机制,使用父元素这个样式的属性值。
<body>
<style>
p {
color: white;
background: grey;
border: medium solid black;
}
span {
border: inherit; /* 继承父元素的boder属性 */
}
</style>
<p>
I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.
</p>
</body>

# CSS中的颜色
css中有三种常用的设置颜色方法
- 直接使用颜色名称
- 设置十六进制RGB值,#000000 (等价于0, 0, 0) #ffffff (等价于255,255,255)
- 使用rgb和rgba函数已10进制来表示颜色 rgb(0,0,0), rgb(255,255,255), rgba(0,0,0,0.3) ,rgba最后一位表示透明度,1为不透明。
- hsl和hsla 使用色相、饱和度、明度表示颜色(用的比较少)hsl(120,100%,22%)
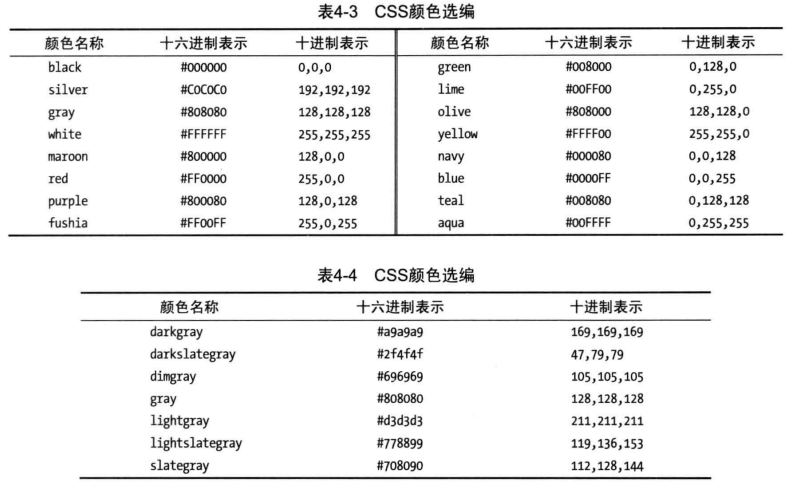
CSS颜色函数

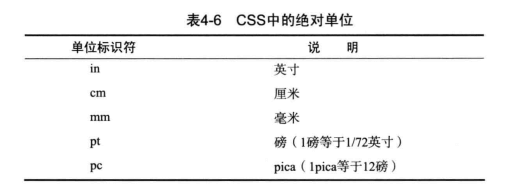
# CSS中的长度
许多css属性要求设置长度值,比如width,font-size。
# 绝对长度
pt、cm、mm
<body>
<style>
.myclass1 {
font-size: 20pt;
}
.myclass2 {
font-size: 2cm; /* 20mm */
color: red;
}
</style>
<p>
1.I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.
</p>
<p class="myclass1">
2.I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.(font-size:20pt)
</p>
<p class="myclass2">
3.I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.(font-size:2cm或20mm)
</p>
</body>
示例

# 相对长度
em, rem, px, %,
- em表示相对当前元素字体的倍数,rem表示相对根元素(html)字体的倍数。
- %百分比如果是font-size挂钩的是父元素的font-size的百分比,如果是width,挂钩的是元素包含块的宽度
- vh viewport视口高度,一般height可以设置为 html {min-height:100vh}
- vw 视口宽度(1vw = 1%)。不过一般默认宽度就是100%,宽度用百分比多。高度是由于默认高度不是100%,如果需要表示全屏,使用100vh会比较方便。

示例:
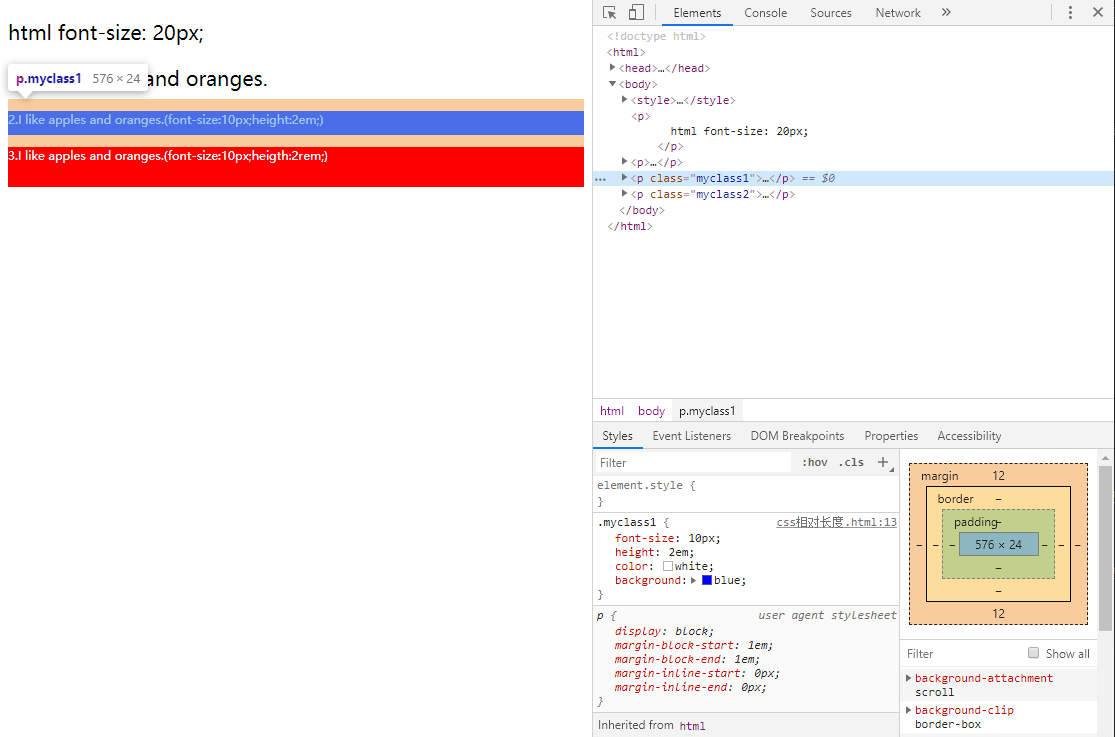
<body>
<style>
html {
font-size: 20px;
}
.myclass1 {
font-size:10px;
height: 2em;
color: white;
background: blue;
}
.myclass2 {
font-size:10px;
height: 2rem;
color:white;
background: red;
}
</style>
<p>
html font-size: 20px;
</p>
<p>
1.I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.
</p>
<p class="myclass1">
2.I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.(font-size:10px;height:2em;)
</p>
<p class="myclass2">
3.I like <span>apples</span> and oranges.(font-size:10px;heigth:2rem;)
</p>
</body>

# calc计算长度
calc可以使用百分比减去固定的px长度
<head>
<style>
div {
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
margin-top: 20px;
border: thin solid #ccc;
}
.cc {
color: red;
width: calc(100% - 100px); /* 注意没空格会无效 calc(100%-100px); */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cc">c1</div>
<div>c2</div>
</body>

# 其他CSS单位
# css角度
一般在transform旋转(rotate)一个元素时,会用到旋转多少度,deg就表示度数。0-360deg
p {
transform: rotate(7deg);
}

# css时间
一般动画时持续时间,可以用秒s或毫秒ms,表示事件间隔

# 有用的CSS工具
# F12浏览器调试
# 使用css预处理器
原生的css暂时无法定义变量,可复用性低,用预处理器还支持嵌套写法。更简洁,更利于维护。
- sass
- less
- stylus
参考: