# Node.js 内置模块笔记
参考
# child_process
child_process 模块允许打开一个子进程去执行其他任务,该功能使 node 程序可以执行指定的 shell 脚本,可以用于自动化部署、定时任务
const { spawn } = require('child_process');
const ls = spawn('ls', ['-lh', '/usr']); // 执行 ls -lh /usr 命令
ls.stdout.on('data', (data) => {
// ls 产生的 terminal log 在这里 console
console.log(`stdout: ${data}`);
});
ls.stderr.on('data', (data) => {
// 如果发生错误,错误从这里输出
console.error(`stderr: ${data}`);
});
ls.on('close', (code) => {
// 执行完成后正常退出就是 0
console.log(`child process exited with code ${code}`);
});
执行写好的 shell 脚本
# deploy.sh
# chmod +x deploy.sh 注意要加可执行权限
# 执行 ./deploy.sh 或者 sh ./deploy.sh
echo "开始部署"
# 显示当前执行路径,用于排查路径错误
pwd
# 拉取最新代码
git pull
# pm2 重启服务 node 服务,也可以是其他逻辑
pm2 stop xxx
pm2 start src/index.js -n 'xxx'
echo "完成部署"
用于执行 shell 脚本的 node 程序
// deploy.js
const { spawn } = require('child_process');
const child = spawn('sh', ['./deploy.sh']); // sh ./deploy.sh 运行脚本
child.stdout.on('data', (data) => {
// 运行命令产生的 terminal log 在这里 console
console.log(`stdout: ${data}`);
});
child.stderr.on('data', (data) => {
// 如果发生错误,错误从这里输出
console.error(`stderr: ${data}`);
});
child.on('close', (code) => {
// 执行完成后正常退出就是 0
console.log(`child process exited with code ${code}`);
});
# http
# http.ClientRequest 类 http.get()、http.request()
可以使用 http.get()、http.request() 发送 http 请求。这两个函数返回 http.ClientRequest 对象
http.request(url[, options][, callback])发送 http 请求http.get(url[, options][, callback])发送 get 请求方式的 http 请求,自动调用 req.end()
http.ClientRequest 对象(假设命名为 request,一般简写为 req) 支持以下方法、事件
request.write(chunk[, encoding][, callback])Sends a chunk of the body 发送一个请求主体(body)的数据块。POST 传送数据时使用request.end([data[, encoding]][, callback])完成发送请求。 req.end(data, encoding, cb) 相当于调用 req.write(data, encoding) 后再调用 req.end(cb)request.destroy([error])销毁请求,用于替代之前的 request.abort()error 事件req.on('error', cb) 如果请求出错,需要监听该事件接收错误,使用 try/catch 是无法捕获错误的。
发送 GET 请求
const http = require('http')
const req = http.request('http://fe.zuo11.com', {
// hostname: 'localhost',
// port: 80,
// agent: false, // 是否使用代理
path: '/'
}, (res) => {
const { statusCode } = res;
const contentType = res.headers['content-type'];
console.log(statusCode, contentType) // 200 text/html; charset=utf-8
res.setEncoding('utf8');
let rawData = '';
res.on('data', (chunk) => { rawData += chunk; });
res.on('end', () => {
// res 文本数据,如果是 JSON 字符串数据,需使用 JSON.parse(rawData);
console.log(rawData)
});
}).on('error', (e) => {
// 请求返回的 http.ClientRequest 类,可以监听上面的一些方法
console.error(`请求出现错误: ${e.message}`);
});
req.end() // 必须
由于大多请求是不带请求体(body data)的 GET 请求,于是 Node.js 提供了更便捷的 http.get() 方法,和 http.request 的区别是无法设置 method 为 POST 等,而且内部会自动调用 req.end() 完成发送请求。
const http = require('http')
http.get('http://fe.zuo11.com', {
// hostname: 'localhost',
// port: 80,
// agent: false, // 是否使用代理
path: '/'
}, (res) => {
const { statusCode } = res;
const contentType = res.headers['content-type'];
console.log(statusCode, contentType) // 200 text/html; charset=utf-8
res.setEncoding('utf8');
let rawData = '';
res.on('data', (chunk) => { rawData += chunk; });
res.on('end', () => {
// res 文本数据,如果是 JSON 字符串数据,需使用 JSON.parse(rawData);
console.log(rawData)
});
}).on('error', (e) => {
// 请求返回的 http.ClientRequest 类,可以监听上面的一些方法
console.error(`请求出现错误: ${e.message}`);
});
发送 POST 请求,如果需要在请求体携带数据,注意设置 Content-Type 请求头
const http = require('http')
const querystring = require('querystring')
const req = http.request('http://127.0.0.1', {
path: '/user',
port: 8000,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
// 'Content-Length': Buffer.byteLength(postData)
'Referer': 'www.zuo11.com'
}
}, (res) => {
// res IncomingMessage
const { statusCode } = res;
const contentType = res.headers['content-type'];
console.log(statusCode, contentType) // 200 application/json; charset=utf-8
res.setEncoding('utf8');
let rawData = '';
res.on('data', (chunk) => { rawData += chunk; });
res.on('end', () => {
// res 文本数据,如果是 JSON 字符串数据,需使用 JSON.parse(rawData);
console.log(rawData) // {"code":200,"msg":"Success","data":{"b":1}}
});
}).on('error', (e) => {
// 请求返回的 http.ClientRequest 类,可以监听上面的一些方法
console.error(`请求出现错误: ${e.message}`);
});
// req.write(JSON.stringify({ a: 1, b: 2 }))
req.write(querystring.stringify({ a: 1, b: 2 })) // 'a=1&b=2'
req.end() // 必须
对应的 koa 接口服务
const Koa = require('koa')
const Router = require('koa-router')
const app = new Koa()
app.use(require('koa-bodyparser')())
const router = new Router()
router.post('/user', ctx => {
console.log(ctx)
console.log(ctx.request.body)
ctx.body = {
code: 200,
msg: 'Success',
data: {
b: 1
}
}
})
app.use(router.routes())
app.listen(8000, () => console.log('server listen on 8000 port'))
注意:使用 http 模块发送请求时,可以伪造 Referer。上面的测试中,在 Koa 里可以接收到 headers 参数
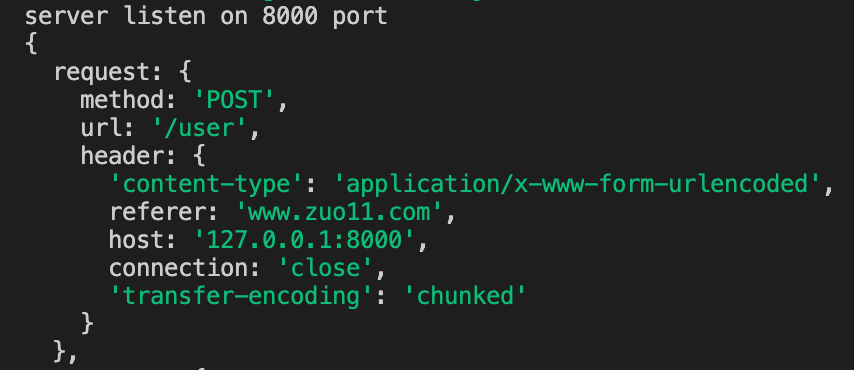
# http.Server 类 http.createServer()
http 模块除了可以发送 http 请求外,还可以使用创建 http 服务,监听处理 http 请求。使用 http.createServer() 创建 http 服务,返回 http.Server 实例,该实例调用 listen 方法开始监听服务
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// console.log('req', req) // req IncomingMessage
// console.log('res', res) // res ServerResponse
res.end('123'); // 接收到请求后,返回 "123"
});
console.log(server)
server.on('clientError', (err, socket) => {
socket.end('HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request\r\n\r\n');
});
server.listen(8000);
# http.ServerResponse 类
http.createServer 用于 http 模块在接收到 http 请求后,响应数据。是 http.createServer() 回调函数的第二个参数。
// http.ServerResponse 类实例 response
response.end([data[, encoding]][, callback])
# http.IncomingMessage 类
http.IncomingMessage 类有两个常见的用处
- 在接收到 http 请求时,用于接收请求信息,是 http.createServer() 回调函数的第一个参数。
- 在发送 http 请求后,用于接收响应数据,是http.request() 和 http.get() 回调函数的参数
用法大致如下
const http = require('http')
const querystring = require('querystring')
const req = http.request('http://127.0.0.1', {
path: '/',
}, (res) => {
console.log(res) // IncomingMessage
const { statusCode } = res;
const contentType = res.headers['content-type'];
console.log(statusCode, contentType)
res.setEncoding('utf8');
let rawData = '';
res.on('data', (chunk) => { rawData += chunk; });
res.on('end', () => {
console.log(rawData)
});
}).on('error', (e) => {
// 请求返回的 http.ClientRequest 类,可以监听上面的一些方法
console.error(`请求出现错误: ${e.message}`);
});
req.end() // 必须
# http.METHODS、http.STATUS_CODES
http 模块包含两个常量属性,分别表示支持 http 请求方法,http 响应状态码集合。
METHODS: [
'ACL', 'BIND', 'CHECKOUT',
'CONNECT', 'COPY', 'DELETE',
'GET', 'HEAD', 'LINK',
'LOCK', 'M-SEARCH', 'MERGE',
'MKACTIVITY', 'MKCALENDAR', 'MKCOL',
'MOVE', 'NOTIFY', 'OPTIONS',
'PATCH', 'POST', 'PROPFIND',
'PROPPATCH', 'PURGE', 'PUT',
'REBIND', 'REPORT', 'SEARCH',
'SOURCE', 'SUBSCRIBE', 'TRACE',
'UNBIND', 'UNLINK', 'UNLOCK',
'UNSUBSCRIBE'
],
STATUS_CODES: {
'100': 'Continue',
'101': 'Switching Protocols',
'102': 'Processing',
'103': 'Early Hints',
'200': 'OK',
'201': 'Created',
'202': 'Accepted',
'203': 'Non-Authoritative Information',
'204': 'No Content',
'205': 'Reset Content',
'206': 'Partial Content',
'207': 'Multi-Status',
'208': 'Already Reported',
'226': 'IM Used',
'300': 'Multiple Choices',
'301': 'Moved Permanently',
'302': 'Found',
'303': 'See Other',
'304': 'Not Modified',
'305': 'Use Proxy',
'307': 'Temporary Redirect',
'308': 'Permanent Redirect',
'400': 'Bad Request',
'401': 'Unauthorized',
'402': 'Payment Required',
'403': 'Forbidden',
'404': 'Not Found',
'405': 'Method Not Allowed',
'406': 'Not Acceptable',
'407': 'Proxy Authentication Required',
'408': 'Request Timeout',
'409': 'Conflict',
'410': 'Gone',
'411': 'Length Required',
'412': 'Precondition Failed',
'413': 'Payload Too Large',
'414': 'URI Too Long',
'415': 'Unsupported Media Type',
'416': 'Range Not Satisfiable',
'417': 'Expectation Failed',
'418': "I'm a Teapot",
'421': 'Misdirected Request',
'422': 'Unprocessable Entity',
'423': 'Locked',
'424': 'Failed Dependency',
'425': 'Unordered Collection',
'426': 'Upgrade Required',
'428': 'Precondition Required',
'429': 'Too Many Requests',
'431': 'Request Header Fields Too Large',
'451': 'Unavailable For Legal Reasons',
'500': 'Internal Server Error',
'501': 'Not Implemented',
'502': 'Bad Gateway',
'503': 'Service Unavailable',
'504': 'Gateway Timeout',
'505': 'HTTP Version Not Supported',
'506': 'Variant Also Negotiates',
'507': 'Insufficient Storage',
'508': 'Loop Detected',
'509': 'Bandwidth Limit Exceeded',
'510': 'Not Extended',
'511': 'Network Authentication Required'
}
# https
http 模块不支持发送 https 请求,不支持监听 https 服务。这就需要使用 https 模块了。
发送 https 请求,和 http 模块基本一致,将 https 换成 http 即可,注意 options 里面的 port 默认为 443
在创建 https 服务时,需要增加 SSL 证书相关文件
const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
const options = {
key: fs.readFileSync('test/fixtures/keys/agent2-key.pem'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('test/fixtures/keys/agent2-cert.pem')
};
// 或者
// const options = {
// pfx: fs.readFileSync('test/fixtures/test_cert.pfx'),
// passphrase: '密码'
// };
https.createServer(options, (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200);
res.end('你好,世界\n');
}).listen(8000);
# http2
由于 HTTP/2 相比 HTTP 1.x 增加了很多特殊处理,需要使用专门的 http2 模块来处理。HTTP/2 必须是 https,不支持 http
客户端发送 http 请求
const http2 = require('http2');
const fs = require('fs');
const client = http2.connect('https://localhost:8443', {
ca: fs.readFileSync('证书.pem')
});
client.on('error', (err) => console.error(err));
const req = client.request({ ':path': '/' });
req.on('response', (headers, flags) => {
for (const name in headers) {
console.log(`${name}: ${headers[name]}`);
}
});
req.setEncoding('utf8');
let data = '';
req.on('data', (chunk) => { data += chunk; });
req.on('end', () => {
console.log(`\n${data}`);
client.close();
});
req.end();
创建监听 http 服务
const http2 = require('http2');
const fs = require('fs');
const server = http2.createSecureServer({
key: fs.readFileSync('密钥.pem'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('证书.pem')
});
server.on('error', (err) => console.error(err));
server.on('stream', (stream, headers) => {
// 流是一个双工流。
stream.respond({
'content-type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8',
':status': 200
});
stream.end('<h1>你好世界</h1>');
});
server.listen(8443);
# querystring
可以用于发送 Content-Type 为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 时的数据处理
const querystring = require('querystring');
querystring.stringify({ foo: 'bar', baz: ['qux', 'quux'], corge: '' });
// 返回 'foo=bar&baz=qux&baz=quux&corge='
querystring.stringify({ foo: 'bar', baz: 'qux' }, ';', ':');
// 返回 'foo:bar;baz:qux'
querystring.parse('foo=bar&abc=xyz&abc=123')
// {
// foo: 'bar',
// abc: ['xyz', '123']
// }
# dns
# dns.lookup()
DNS 查询,根据 hostname(主机名) 获取 IP 地址以及对应的版本。内部使用 getaddrinfo 系统调用,会读取 /etc/hosts 的配置
// dns.js
const dns = require('dns');
// 注意不能使用 http 等协议
const arr = [
'www.zuo11.com',
'fe.zuo11.com'
]
arr.forEach(host => {
// dns 查询,
dns.lookup(host, (err, address, family) => {
console.log('host: %j \naddress: %j family: IPv%s', host, address, family);
});
})
// node dns.js
// host: "fe.zuo11.com"
// address: "120.77.166.5" family: IPv4
// host: "zuo11.com"
// address: "47.107.190.93" family: IPv4
# dns.resolveAny()
DNS 解析记录查询,比 dns.lookup() 查询的信息更详细,准确。忽略 /etc/hosts 的配置,始终通过网络执行 DNS 查询。可以根据 hostname 获取对应的解析类型、解析值。
const dns = require('dns');
// 注意不能使用 http 等协议
const arr = [
'www.zuo11.com',
'fe.zuo11.com'
]
arr.forEach(host => {
dns.resolveAny(host, (err, ret) => {
console.log(err, ret)
})
})
// null [
// { value: 'fe-zuo11-com.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com', type: 'CNAME' }
// ]
// null [ { address: '47.107.190.93', ttl: 600, type: 'A' } ]
除了 dns.resolveAny() 外,还有粒度更细的相关 API,参考 ns_dns_resolve_hostname (opens new window)
dns.resolveAny()Uses the DNS protocol to resolve all records (also known as ANY or * query).dns.resolve4()Uses the DNS protocol to resolve a IPv4 addresses (A records) for the hostname.dns.resolve6()Uses the DNS protocol to resolve a IPv6 addresses (AAAA records) for the hostname.dns.resolveCname()Uses the DNS protocol to resolve CNAME records for the hostname.dns.resolveNs()Uses the DNS protocol to resolve name server records (NS records) for the hostname.- ...
# dns.reverse()
反向 DNS 查询
const ipArr = [
'47.107.190.93',
]
ipArr.forEach(ip => {
// 使用 getHostByAddr 系统调用
// 执行一个反向 DNS 查询,将 IPv4 或 IPv6 地址解析为主机名数组。
dns.reverse(ip, (err, hostnames) => {
console.log('dns.reverse', err, hostnames)
})
})
一般服务供应商不允许反向 DNS 查询,会报错 Error: getHostByAddr ENOTFOUND 47.107.190.93,参考: Firebase reverse dns lookup ENOTFOUND error node.js dns (opens new window)
// dns.reverse Error: getHostByAddr ENOTFOUND 47.107.190.93
// at QueryReqWrap.onresolve [as oncomplete] (dns.js:203:19) {
// errno: 'ENOTFOUND',
// code: 'ENOTFOUND',
// syscall: 'getHostByAddr',
// hostname: '47.107.190.93'
// } undefined
// don't allow reverse DNS lookups
参考: DNS | Node.js v14.15.4 Documentation (opens new window)
# dns.getServers()
返回 IP 地址字符串的数组,该字符串根据 RFC 5952 进行了格式化,作为当前 DNS 解析。如果使用自定义端口,则字符串将包含端口部分。
console.log(`dns.getServers()`, dns.getServers())
// dns.getServers() [ '192.168.31.1' ] 本地路由地址
# dns Promise 形式接口
使用 require('dns').promises 相当于之前的 dns,相关 API 都是 Promise 形式
const dnsPromises = require('dns').promises
dnsPromises.lookup('fe.zuo11.com').then((result) => {
console.log('address: %j family: IPv%s', result.address, result.family);
// address: "120.77.166.5" family: IPv4
});
dnsPromises.resolveAny('fe.zuo11.com').then((ret) => {
console.log(ret)
});
// [
// { value: 'fe-zuo11-com.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com', type: 'CNAME' }
// ]
dnsPromises.reverse('120.77.166.5').then(console.log).catch(err => {
console.log(err) // 错误
})
// Error: getHostByAddr ENOTFOUND 120.77.166.5