# CSS 预处理器 Less.js
参考:Less.js 官网 (opens new window)、Less.js | Github (opens new window)
# 为什么会有 Less.js
CSS 是一种文件样式计算机语言,它不足的地方:
- 缺少编程特性,比如变量、函数、逻辑控制语句等,代码冗余度高。
- 模块化程度低,代码碎片化、零散,不便于维护
- 注释只支持 /**/
Less(which stands for Leaner Style Sheets) 是一种 CSS 语言的扩展,由 JS 编译处理。使用 Less 语法写的样式文件,后缀名为 .less。
它在 CSS 的基础上新增了一些新的语法特性,算是一种新的计算机语言。在一定程度上弥补了 CSS 的不足,使 CSS 写法更加精简、高效。它的特点:
- 加入了一些编程特性,比如:变量、Mixin、函数、命名空间、流程控制等,提高函数复用、减少重复代码
- 支持嵌套(Nesting)写法,代码更加模块化,方便维护
- 除了支持 /**/ 注释外,还支持 // 注释
# Less.js 使用方法
Node.js 环境
# 安装 Less npm 包 npm install -g less # 将 less 文件转为 css 文件 > lessc styles.less styles.cssbrowser 浏览器环境
<!-- 按照 less语法写的样式文件 --> <link rel="stylesheet/less" type="text/css" href="styles.less" /> <script src="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/less" ></script>
在 node 工程化使用场景中,less 代码会被编译为 css 代码。
在浏览器中环中,运行的时候 Less.js 会读取 .less 代码,并编译为 CSS 代码,再创建动态的 style 元素,使样式生效。
注意:link 的 rel 为 stylesheet/less,具体执行过程,可以看 less.js 在 Github 上的源码。
# Less 基础语法
# 注释(Comments)
/* 一般 css 注释 */
// less支持 // 注释
a {
color: green;
}
# 引入(Importing)
@import "lib"; // lib.less
@import "common.css";
# 变量(Variables)
可以使用 @变量名: 对应值; 的语法定义一个变量。使用变量直接使用 @变量名 即可
// styles.less
@height: 100px;
@myColor: red;
#my-div {
height: @height;
background: @myColor;
}
使用 lessc styles.less styles.css 生成的 css 代码如下
#my-div {
height: 100px;
background: red;
}
上面的变量都是独立使用的,变量也可以与其他字符串结合使用,它的语法是 @{变量名}
// 选择器
@my-selector: my-div;
.@{my-selector} {
color: red;
}
// URL
@images: "../images";
div {
background: url("@{images}/test.png");
}
// 属性名
@property: color;
.widget {
@{property}: #0ee;
background-@{property}: #999;
}
输出:
.my-div {
color: red;
}
div {
background: url("../images/test.png");
}
.widget {
color: #0ee;
background-color: #999;
}
尽管 CSS 原生支持 变量,可以使用 --变量名: 对应值; 语法定义变量,使用时用 val(--变量名),但它不支持 IE。目前来看,使用预处理器还是要好一点。
/* 最大高度为三行,将line-height定义为变量lh */
.module {
--lh: 1.2rem;
line-height: var(--lh);
max-height: calc(var(--lh) * 3);
overflow: hidden;
}
# 操作符(Operations)
对于宽高百分比等尺寸单位,可以使用算术操作符 + - x / 进行运算
@height: 100px;
@width: @height + 50px;
#operations-test {
width: @width * 2;
height: @height / 3;
}
输出:
#operations-test {
width: 300px;
height: 33.33333333px;
}
# 嵌套写法(Nesting)
对于同一模块,我们一般会分为几个部分,一般通用的 CSS 写法如下
.container {
color: black;
}
.container .left {
width: 300px;
}
.container .left span {
color: red;
}
.container .right {
width: calc(100% - 300px);
}
可以看到需要些很多重复的 class,而且层级结构不突出,代码零散,不容易维护。less 支持嵌套写法,下面是用 Less 重构后的代码
@leftWidth: 300px;
.container {
color: black;
.left {
width: @leftWidth;
span {
color: red;
}
}
.right {
width: calc(100% - @leftWidth)
}
}
这样结构层次分明、模块化程度高,可维护性好。Less 编译后的代码与上面 CSS 的代码完全一致。
嵌套写法如果需要写对应的 hover 样式等,就需要使用 父元素选择器 & 了。
.btn {
color:#666;
&:hover {
border: 1px solid red;
}
&-primary {
color: blue;
}
&-danger {
color: red;
}
}
输出:
.btn {
color: #666;
}
.btn:hover {
border: 1px solid red;
}
.btn-primary {
color: blue;
}
.btn-danger {
color: red;
}
# 混入(Mixins)
可以将一个样式规则.类名 { } 或 #id名 { },或一组样式规则 .类名() { } 或 #id名() { },使用 .类名() 或 #ID名() 混入到另一组规则中。
// 单个样式规则混入
.classtest {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#idtest {
margin-top: 10px;
}
#a span {
.classtest();
#idtest();
color: blue;
}
.tips {
.classtest();
#idtest();
}
输出
.classtest {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#idtest {
margin-top: 10px;
}
#a span {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
margin-top: 10px;
color: blue;
}
.tips {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
margin-top: 10px;
}
一组、多个样式规则混入时,还可以使用对应的选择器来进行选择性混入。
// 一组 多个样式混入
.grouptest() {
a {
color: red;
}
.btn {
width: 100px;
}
}
.some {
.grouptest();
}
.some2 {
.grouptest.btn();
}
输出:
.some a {
color: red;
}
.some .btn {
width: 100px;
}
.some2 {
width: 100px;
}
另外 3.5+ 版本,混入还可以结合 Map 使用
// mixins map用法
#colors() {
primary: blue;
success: green;
}
.btn {
color: #colors[primary];
border: 1px solid #colors[success];
}
输出:
.btn {
color: blue;
border: 1px solid green;
}
# 键值对(Maps)
除了在混入里面可以有 Map 类型的数据外,也可以使用 @变量名: { key: value, key2: value2 } 来定义 Map,使用 @变量名[key] 来获取 Map 值
@sizes: {
a: 320px;
b: 768px;
c: 1024px;
}
.test {
width: @sizes[a];
height: @sizes[b]
}
输出
.test {
width: 320px;
height: 768px;
}
# 转义(Escaping)
转义可以将任意字符串用作属性或变量名,使用 ~"任意字符串" 会原样输出
@min768: ~"(min-width: 768px)";
// @min768: (min-width: 768px); // less 3.5+ 可以直接这样使用
@media @min768 {
a {
color: blue;
}
}
輸出:
@media (min-width: 768px) {
a {
color: blue;
}
}
# 函数(Functions)
Less 内置了一些系统函数,比如逻辑控制函数 if,列表函数 each,数学函数 round,颜色操作函数 lighten、darken 等,这里主要介绍一些比较常见的函数
# 类型判断函数(Type Functions)
这里只简单介绍三个类型判断函数:isnumber(值)、isstring(值)、iscolor(值),他们的返回值是 Boolean 类型:true or false
isnumber(blue); // false
isnumber(1234); // true
isnumber(56px); // true
isnumber(7.8%); // true
isstring(blue); // false
isstring("string"); // true
iscolor(#ff0); // true
iscolor(blue); // true
iscolor("string"); // false
# 逻辑函数(Logical Functions)
if 根据条件返回不同的值,语法:if((表达式), 表达式为true时返回的值, 表达式为false时返回的值)
boolean 存储表达式的状态值到变量:boolean(表达式)
@some: foo;
@result: boolean(isstring(@some));
div {
margin: if((2 > 1), 0, 3px);
color: if((iscolor(@some)), @some, black);
height: if(@result, 100px, 200px)
}
.test {
color: if(not (true), foo, bar);
size: if((true) and (2 > 1), foo, bar);
width: if((false) or (isstring("boo!")), foo, bar);
}
输出
div {
margin: 0;
color: black;
height: 200px;
}
.test {
color: bar;
size: foo;
width: foo;
}
# 列表函数(List Functions)
使用逗号或空格分隔的数据就是 list,先来看列表相关的基础函数
length(列表),返回列表长度extract(列表, index),用 index 取列表里的值,注意:index 从 1 开始range(可选的 start, end, 可选的 step),创建一个 list 列表
@colors: red, rgb(30, 30, 31), yellow;
@list: 768px 1024px 1366px 1920px;
.btn {
width: length(@colors);
height: length(@list);
}
span {
// extract 从 1 开始
color: extract(@colors, 3);
width: extract(@colors, 1);
padding: range(4);
margin: range(10px, 30px, 10);
}
输出:
.btn {
width: 3;
height: 4;
}
span {
color: yellow;
width: red;
padding: 1 2 3 4;
margin: 10px 20px 30px;
}
each 是对列表、键值对的遍历,并将里面的每个值绑定到对应规则集(ruleset)里。 each(列表或者Map键值对, 一个匿名的 ruleset 或 mixins)
@selectors: blue, green, yellow;
each(@selectors, {
.btn-@{value} {
color: @value;
}
})
@set: {
one: blue;
two: green;
three: yellow;
}
.set {
each(@set, {
@{key}-@{index}: @value;
})
}
输出
.btn-blue {
color: blue;
}
.btn-green {
color: green;
}
.btn-yellow {
color: yellow;
}
.set {
one-1: blue;
two-2: green;
three-3: yellow;
}
mixins 遍历,指定参数
.set-2() {
one: blue;
two: green;
three: red;
}
.set-2 {
// Call mixin and iterate each rule
each(.set-2(), .(@v, @k, @i) {
@{k}-@{i}: @v;
});
}
输出
.set-2 {
one-1: blue;
two-2: green;
three-3: red;
}
# 数学函数(Math Functions)
@k: ceil(2.4) floor(2.6) round(2.4) round(2.6) percentage(0.5) sqrt(25px) abs(-12%) min(1, 2);
.btn {
each(@k, {
a-@{index}: @value;
})
}
输出
.btn {
a-1: 3;
a-2: 2;
a-3: 2;
a-4: 3;
a-5: 50%;
a-6: 5px;
a-7: 12%;
a-8: 1;
}
# 颜色函数(Color Functions)
lighten(color, 0-100百分比)将颜色亮度调高,变亮darken(color, 0-100百分比)将颜色亮度调低,变暗
@color: #80e619;
@colors: @color lighten(@color, 30) darken(@color, 30);
.btn {
display: inline-block;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
each(@colors, {
.btn-@{index} {
background: @value;
}
})
输出
.btn {
display: inline-block;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
}
.btn-1 {
background: #80e619;
}
.btn-2 {
background: #ccf5a3;
}
.btn-3 {
background: #335c0a;
}
来看个例子
<link rel="stylesheet" href="color.css">
<div>
<div class="btn btn-1"></div>
<div class="btn btn-2"></div>
<div class="btn btn-3"></div>
</div>
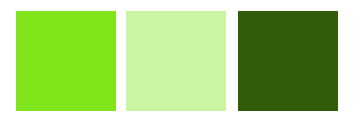
# 作用域(Scope)
嵌套的样式规则里面可以重写(Overwrite)变量的值,有较高的优先级
@var: red;
#page {
@var: white;
#header {
color: @var; // white
}
}
# 深入指南
# @@可变的变量(Variable Variables)
@@变量 可变的变量
@primary: green;
@secondary: blue;
.section {
@color: primary;
.element {
color: @@color;
}
}
输出
.section .element {
color: green;
}
# $属性作为变量(Properties as Variables)
$属性名 可以获取属性的值
.widget {
color: #efefef;
background-color: $color;
}
输出
.widget {
color: #efefef;
background-color: #efefef;
}
# & 父元素选择器组合、顺序等
.link {
// 多个父元素选择器组合
& + & {
color: red;
}
& & {
color: green;
}
// 父元素选择器 放到后面
.test & {
color: blue;
}
}
输出
.link + .link {
color: red;
}
.link .link {
color: green;
}
.test .link {
color: blue;
}
# Less伪类:扩展(Extend)
先来看使用场景,当我们有一个基础的 class 后,像基于基础的 class 再扩展内容,可能会再增加一个 class,而 extend 可以让你只用一个 class 就搞定
<a class="animal bear">Bear</a>
<style>
.animal {
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
.bear {
background-color: brown;
}
</style>
使用 extend 可以减少一个 class
<a class="bear">Bear</a>
<style lang="less">
.animal {
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
.bear {
/* 相当于把 .animal 的样式全部用到 .bear */
&:extend(.animal);
/* &:extend(.animal, all); 如果加了 all 参数就是包含嵌套的样式 */
background-color: brown;
}
</style>
编译后的 CSS
.animal,
.bear {
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
.bear {
background-color: brown;
}
减少 CSS 体积:另外 extend 生成的代码比普通的混入(Mixins)代码更精简
.my-inline-block() {
display: inline-block;
font-size: 0;
}
.thing1 {
.my-inline-block;
}
.thing2 {
.my-inline-block;
}
生成的代码如下,会有重复的
.thing1 {
display: inline-block;
font-size: 0;
}
.thing2 {
display: inline-block;
font-size: 0;
}
使用 extend 优化
.my-inline-block() {
display: inline-block;
font-size: 0;
}
.thing1 {
&:extend(.my-inline-block);
}
.thing2 {
&:extend(.my-inline-block);
}
.my-inline-block,
.thing1,
.thing2 {
display: inline-block;
font-size: 0;
}
# 带参数的混入(Parametric Mixins)
当使用一组样式进行混入时,可以在 () 里面传入变量参数,并设置默认值,作为可选参数
.border-radius(@width: 1px, @color: red, @radius: 5px) {
border: @width solid @color;
border-radius: @radius;
}
.btn {
.border-radius(2px, blue, 10px);
}
.btn-2 {
.border-radius();
}
输出
.btn {
border: 2px solid blue;
border-radius: 10px;
}
.btn-2 {
border: 1px solid red;
border-radius: 5px;
}
# 导入选项(Import Options)
Less 为 @import 提供了一个些参数,已便更加灵活的导入样式文件:@import (keyword) "filename";
keyword
- reference: use a Less file but do not output it
- inline: include the source file in the output but do not process it
- less: treat the file as a Less file, no matter what the file extension
- css: treat the file as a CSS file, no matter what the file extension
- once: only include the file once (this is default behavior)
- multiple: include the file multiple times
- optional: continue compiling when file is not found
这里只重点介绍下 reference 这个选项,加了这个参数后,仅是引用该 CSS,但如果没有使用 extend() 引用里面的样式,就不会编译到输出的 css 文件里。
Use @import (reference) to import external files, but without adding the imported styles to the compiled output unless referenced.
这对想引入一个组件库,但仅仅会用到组件库的一小块样式比较实用。来看个例子:假设我们想引入 test.less 文件,但只用到 .btn-2 的样式。常规的 @import 会把 test.less 整个文件都输出。如果实用 reference 参数加 extend 就可以做到按需引入了。
// test.less
.btn-2 {
color: green;
span {
color: red;
}
}
span {
padding: 10px;
}
reference.less
@import (reference) "test.less";
.btn {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
&:extend(.btn-2);
// &:extend(.btn-2 all); // 如果嵌套的 span 也要输出,加all
}
输出如下,可以看到,仅把 .btn-2 的样式进行输出了,且没有加 all ,这样嵌套的 span 也不会输出
.btn {
color: green;
}
.btn {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}